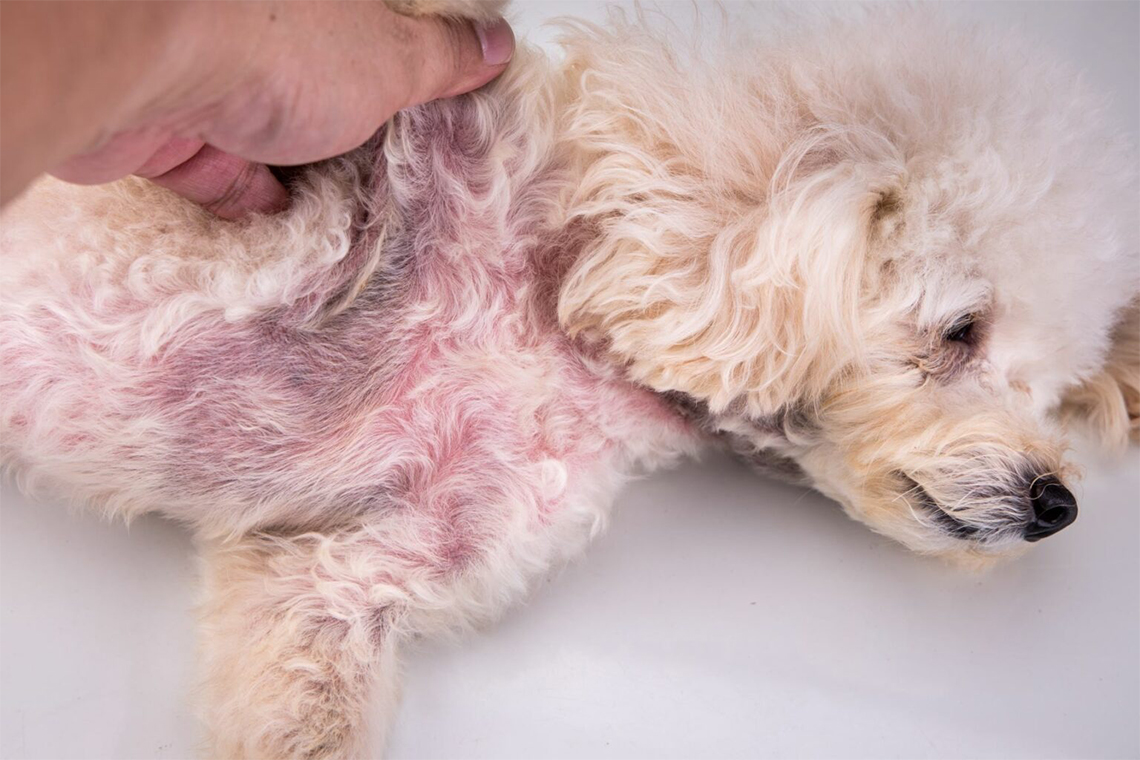
Skin infections are a common health issue that affects dogs of all breeds and ages. These infections can be caused by various factors, including bacterial, fungal, or parasitic infections. Identifying the type of infection your dog has is critical to determining the right treatment plan. In this article, we will discuss the most common skin infections in dogs, their symptoms, causes, and treatment options.
Bacterial Infections
Bacterial infections are one of the most common skin infections in dogs. They occur when bacteria invade the skin, causing redness, swelling, and irritation. The most common bacteria that cause skin infections in dogs are Staphylococcus and Streptococcus. These bacteria can enter the body through a wound, scratch, or insect bite. Dogs with weakened immune systems, allergies, or hormonal imbalances are more susceptible to bacterial infections.
Symptoms of bacterial infections include:
Redness and inflammation of the skin
Pus-filled bumps or blisters
Itching and scratching
Loss of hair around the affected area
Bad odor
Treatment for bacterial infections usually involves antibiotics. Your vet may prescribe a topical or oral antibiotic depending on the severity of the infection. Additionally, you may need to clean the affected area regularly and keep your dog from scratching or biting the infected area to prevent further damage.

Fungal Infections
Fungal infections are another common skin problem in dogs. They occur when fungi invade the skin, hair, or nails. The most common fungi that cause skin infections in dogs are Malassezia and Dermatophytes. These fungi can grow in warm and humid conditions, making dogs living in such environments more susceptible to fungal infections. Dogs with weakened immune systems, allergies, or skin trauma are also more vulnerable.
Symptoms of fungal infections include:
Circular, red, scaly patches on the skin
Crusty, flaky skin
Hair loss
Itching and scratching
Foul odor
Treatment for fungal infections usually involves antifungal medications. Your vet may prescribe topical or oral antifungal drugs depending on the severity of the infection. You may also need to keep your dog’s skin and coat clean and dry to prevent further fungal growth.
Parasitic Infections
Parasitic infections are also common skin infections in dogs. They occur when parasites such as fleas, ticks, or mites infest your dog’s skin. These parasites feed on your dog’s blood, causing redness, itching, and irritation. Dogs living in warm and humid environments are more vulnerable to parasitic infections.
Symptoms of parasitic infections include:
Itching and scratching
Redness and inflammation of the skin
Hair loss around the affected area
Presence of fleas, ticks, or mites on the skin
Scabs and sores
Treatment for parasitic infections usually involves eliminating the parasites from your dog’s skin. This can be done through the use of flea and tick prevention products, as well as regular grooming and cleaning of your dog’s skin and coat. In some cases, your vet may prescribe medication to eliminate the parasites.
Yeast Infections
Yeast infections are caused by an overgrowth of yeast on the skin. The most common type of yeast that causes skin infections in dogs is Malassezia. Yeast infections can occur in any part of the body but are most commonly found in the ears, paws, and skin folds. Dogs with allergies, hormonal imbalances, or compromised immune systems are more susceptible to yeast infections.
Symptoms of yeast infections include:
Itching and scratching
Redness and inflammation of the skin
Oily or greasy skin
Pungent or musty odor
Crusting or scabbing
Treatment for yeast infections usually involves topical or oral antifungal medications. Your vet may also recommend medicated shampoos to help reduce the yeast on your dog’s skin. Additionally, it is important to identify and address any underlying causes of the infection, such as allergies or hormonal imbalances.
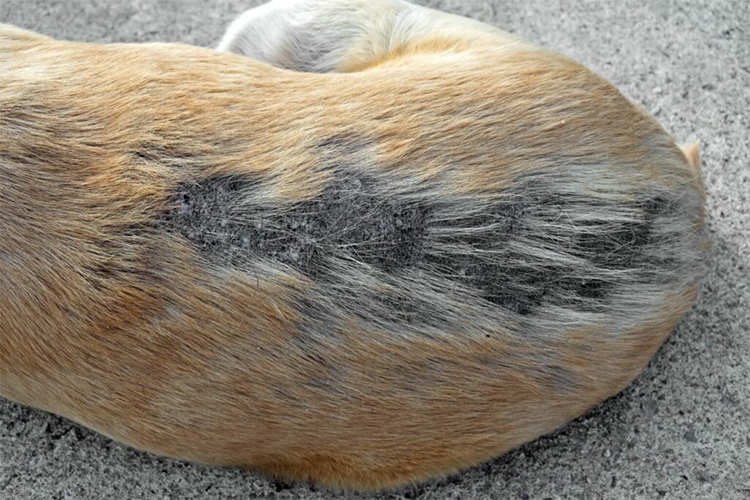

Ringworm
Ringworm is a fungal infection that affects the skin, hair, and nails. It is caused by several types of fungi, including Microsporum and Trichophyton. Ringworm is highly contagious and can be spread from dogs to humans. Dogs with weakened immune systems, poor nutrition, or those living in crowded or unsanitary conditions are more vulnerable to ringworm.
Symptoms of ringworm include:
Circular, red, scaly patches on the skin
Crusty, flaky skin
Hair loss
Itching and scratching
Foul odor
Treatment for ringworm usually involves antifungal medications, as well as good hygiene practices to prevent the spread of the infection. Your vet may recommend isolating your dog from other pets until the infection is under control. Additionally, you may need to clean and disinfect your dog’s bedding and other items regularly to prevent reinfection.
Hot Spots
Hot spots, also known as acute moist dermatitis, are a type of skin infection that occurs when the skin becomes inflamed and infected. Hot spots can be caused by a variety of factors, including allergies, parasites, poor grooming, and skin trauma. Dogs with thick coats, such as Golden Retrievers and German Shepherds, are more susceptible to hot spots.
Symptoms of hot spots include:
Red, oozing, and inflamed skin
Hair loss
Intense itching and scratching
Pungent odor
Treatment for hot spots usually involves cleaning and drying the affected area, as well as topical or oral antibiotics to prevent further infection. Your vet may also recommend identifying and addressing any underlying causes of the hot spots, such as allergies or skin trauma.
Impetigo
Impetigo is a bacterial skin infection that is more commonly seen in puppies than adult dogs. It is caused by Staphylococcus intermedius bacteria and usually affects the skin around the chin, mouth, and nose. Puppies with weakened immune systems or poor hygiene are more susceptible to impetigo.
Symptoms of impetigo include:
Red, crusty, and raised lesions
Pus-filled blisters
Itching and scratching
Hair loss
Treatment for impetigo involves topical or oral antibiotics, as well as keeping the affected area clean and dry. Your vet may recommend regular bathing and grooming to help prevent further infection. It is important to address any underlying issues that may be contributing to the infection, such as poor nutrition or a weakened immune system.
In conclusion, skin infections are a common problem in dogs and can cause discomfort and pain for your furry friend. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical in preventing the infection from spreading and becoming more severe. By practicing good hygiene, providing your dog with proper care, and seeking veterinary advice, you can help keep your dog’s skin healthy and free from infection.